- 1. Agronomy is derived from a Greek word ‘agros’ meaning
‘field’ and ‘nomos’ meaning ‘management’.
Definition of Agronomy
1. It is defined as an agricultural science deals with principles
and practices of crop production and field management.
2. Agronomy is branch of agricultural science, which deals with
principles, & practices of soil, water & crop management.
3. It is branch of agricultural science that deals with methods
which provide favorable environment to the crop for higher
productivity.
- 3. Scope of Agronomy
Identification of proper season for cultivation
Proper methods of cultivation
Availability and application of chemical fertilizers
Availability of herbicides for control of weeds
Water management practices
- 4. Intensive cropping
New technology to overcome the effect of moisture
stress
Packages of practices to explore full potential
Keeping farm implements
Maintaining the ecological balance
Care and disposal of farm and animal products
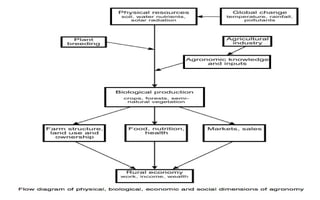
- 5. Relation of agronomy to other sciences
Soil Science
Agricultural Chemistry
Crop physiology
Plant ecology
Biochemistry
Economics
- 6. Crops and major soils - Classification –
Economic and agricultural importance in India
Classification of crops
Classification is done to generalize similar crop plants
as a class for better understanding of them.
Classification types used in crops
1. Based on ontogeny (Life cycle)
2. Based on economic use (Agronomic)
3. Based on Botany (Scientific)
4. Based on seasons 5. Based on climate
- 7. 1. Based on Ontogeny (Life cycle)
a)Annual crops:
Ex. Wheat, rice, maize, mustard etc.
b) Biennial crops:
Ex. Sugar beet, beet root, etc.
c) Perennial crops:
Ex. Napier fodder grass, coconut, etc.
- 8. 2. Based economic use (Agronomic)
Cereals: Cereal derived from word ‘Ceres’ denotes
‘Goddess’
Grasses grown for their edible starchy grains.
Ex: Rice, wheat, maize, barley, oats etc.
Cereal grain contains 60 to 70% of starch
Cereals are an excellent source of fat soluble vitamin E,
Contains 20 to 30% of minerals such as selenium,
calcium, zinc and copper
- 9. b) Millets:
Millets are small grained cereals,
staple food in drier regions poor countries
Millets are broadly classified in to two
1) Major millets and 2) Minor millets
Major millets
1. Sorghum 2. Pearl millet 3. Finger millet or Ragi -
Minor millets
1. Foxtail millet 2. Little millet 3. Common millet
4. Barnyard millet 5. Kodo millet
- 10. c) Pulses:
Rich in protein
Economic important in cropping system
Haulm is used as green manure
Green pods used as vegetables
1. Red gram 2. Black gram 3. Green gram
4. Cowpea 5. Bengalgram 6. Horsegram
7. Lentil 8. Soybean 9. Peas 10. Garden bean 11. Lathyrus
- 11. d) Oil seeds:
Rich in fatty acid
They are used either for edible or industrial or
medicinal purposes
1. Groundnut or peanut 2. Sesame or gingelly
3. Sunflower 4. Castor 5. Linseed or flax 6. Niger
7. Safflower 8. Indian Mustard 9. Sarson
- 12. Groundnut: 1) cooking oil & soap 2) haulm & oil cake is
a used as cattle feed 3)shell has fuel value 4) soil
amendment 5) It is a bed material in the poultry
forms
Sesame: 1) Cooking oil 2) Gingelly cake is used as a
cattle feed 3) Capsule & stalk for composting /
burning purpose
Castor: 1) Oil used as medicinal and industrial oil 2)
Aviation lubricant purpose 3) Castor cake is
concentrated organic manure 4) The shell and stalk is
used for fuel purpose
- 13. Mustard: 1) Edible oil 2) Oil cake cattle feed.
Safflower and sunflower: 1) Oil for cooking purpose
2) Unsaturated fatty acids 3) Cake is used as cattle feed
Niger: 1) Seed used in soap making 2) Paint & varnish
3) light lubricant 4) Crop is generally an industrial crop
Linseed: 1) Oil used in preparation of paints 2)
varnishes
- 14. e) Sugar crops
1)Sugar cane juice used for jaggery or sugar. 2) molasses,
bagasse, pressmud 3) Molasses used for alcohol and
yeast formation 4) bagasse for paper making & fuel. 5)
Press mud used for soil amendment 6) Green leaf & dry
foliage is used for cattle feed.
1) Sugar beet tubers are mainly used for extraction of
sugar 2) Tubers & tops used as a fodder for cattle feed.
- 15. f) Fibre crops: i) seed fibre – cotton; ii) Stem/ bast fibre –
Jute, mesta; iii) leaf fibre – Agave, pineapple.
Cotton: Epidermal hairs of seed coats is the economic
portion. Lint (Kapas-seed) has industrial value (fibre)
Jute, Sunnhemp, mesta: The fibre obtained from stems is
used for gunny bags, ropes. Stem itself is used as fuel.
Sunnhemp is used for both stem fibre and green
manure crop
- 16. g) Fodder / Forage: It refers to vegetative matter, fresh or
preserved, utilized as feed for animals. It includes hay,
silage, pasturage and fodder.
1. Grasses - Bajra napier grass, guinea grass, fodder
sorghum, fodder maize. 2. Legumes - Lucerne,
Desmanthus, etc.
h) Spices and condiments: Ex.– Ginger, garlic, fenugreek,
cumin, turmeric, chillies, onion, coriander,
- 17. i) Medicinal plants: Ex. Tobacco, mint. etc.
j) Beverages: Products of crops used for preparation of
mild, agreeable and simulating drinking.
Ex. Tea, coffee, cocoa (Plantation crops).
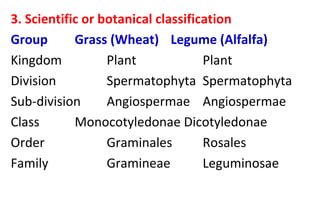
- 18. 3. Scientific or botanical classification
Group Grass (Wheat) Legume (Alfalfa)
Kingdom Plant Plant
Division Spermatophyta Spermatophyta
Sub-division Angiospermae Angiospermae
Class Monocotyledonae Dicotyledonae
Order Graminales Rosales
Family Gramineae Leguminosae
- 19. a) Kharif crops: June-July to September–October
Ex. Rice, maize, castor, groundnut.
b) Rabi crops: October–November to January-February
Ex. Wheat, mustard, barley, oats, potato, bengal gram,
berseem, cabbage and cauliflower.
c) Summer crops: February–March to May–June
Ex.Black gram, greengram, seasome, cowpea etc.
Ex. Kharif rice, kharif maize, rabi maize, summer pulse
- 20. 5. Based on climatic condition
1) Tropical crop : Coconut, sugarcane
2) Sub-tropical crop : Rice, cotton
3) Temperate crop : Wheat, barley
4) Polar crop : All pines, pasture grasses